Indentify the following phases of Meiosis
Phase 1 ______ |
 |
Phase 2 _________ |
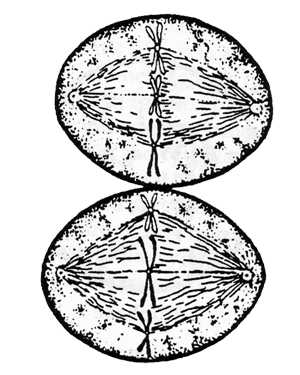 |
Phase 3 ______ |
 |
Phase 4_______ |
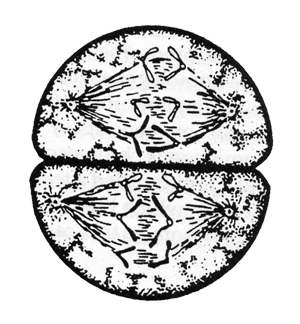 |
Phase 5 ______ |
 |
Phase 6 ________ |
 |
Phase 7 _____ |
 |
||
8. In what phase of meiosis do the chromatids break apart?___________________________________.
9. In what phase(s) of meiosis is (are) there four times as many chromosomes as normal? ______________________
10. In the final phase of meiosis, the cells are (tetraploid, diploid or haploid)? _________________________________
11. In the last phase of meiosis, how many of the resulting cells are identical?_____________________________________
12. In what cells does meiosis occur in people? ____________________________________________
13. What is a zygote? __________________
14. In which process (mitosis, meiosis,or both) does crossing-over occur?____________________________
15. Alternate forms of a gene are called__________________
16. Two genes which are the same are (heterozygous or homozygous)______________.
17. The actual appearance of a trait is called its______________________________.
18. The genetic makeup of a trait is called its ________________________________.
19. Of all the chromosomes you have in each cell, what percentage is from the your father?___________________________
21. A cross involving an incompletely dominant trait where both parents are heterozygous, what would the resulting phenotype ratio be? __________________
22. If a disorder is completely recessive (tt), what must the normal parents be in order for the child to show the disorder? Father ________ Mother _______
23. If attached ear lobes (l) is recessive and free ear lobes (L) is dominate, what would the parents genetic makeup be for both attached and free ear lobes to show up in the children? Father ____________ Mother _______________
24. Can an egg cell contain paternal chromosomes? _____________________
25. What is the centromere? ______________________
Wife ________________ Husband ______________ Children ____________________________
Blood Type |
Antigen |
Antibody Against |
Genotype |
A |
A |
B |
|
B |
B |
A |
|
AB |
A, B |
- |
|
O |
- |
A, B |
28. Name the universal blood type donar (can be given to anyone) __________________
29. Name the universal blood type receiver (can be received from anyone) ___________
30. Which blood type shows the co-dominace the best? _______________